Post-2026 Draft EIS Alternatives
Supply-Driven Alternative
Annual Lake Powell releases are determined based on a 65 percent of 3-year-average natural flow at Lees Ferry. Lake Powell elevations could be increased by releases from CRSP Upper Initial Units within their respective RODs to protect infrastructure at Glen Canyon Dam. This alternative would include new delivery and storage mechanisms for Lake Powell and Lake Mead. Lower Basin shortages up to 2.1 maf would be triggered based on Lake Mead elevation. This alternative analyzes two approaches to shortage distribution: state-based combined with Lower Basin-wide priority and state-based combined with Lower Basin-wide pro rata.
Shortage Guidelines to Reduce Deliveries from Lake Mead³
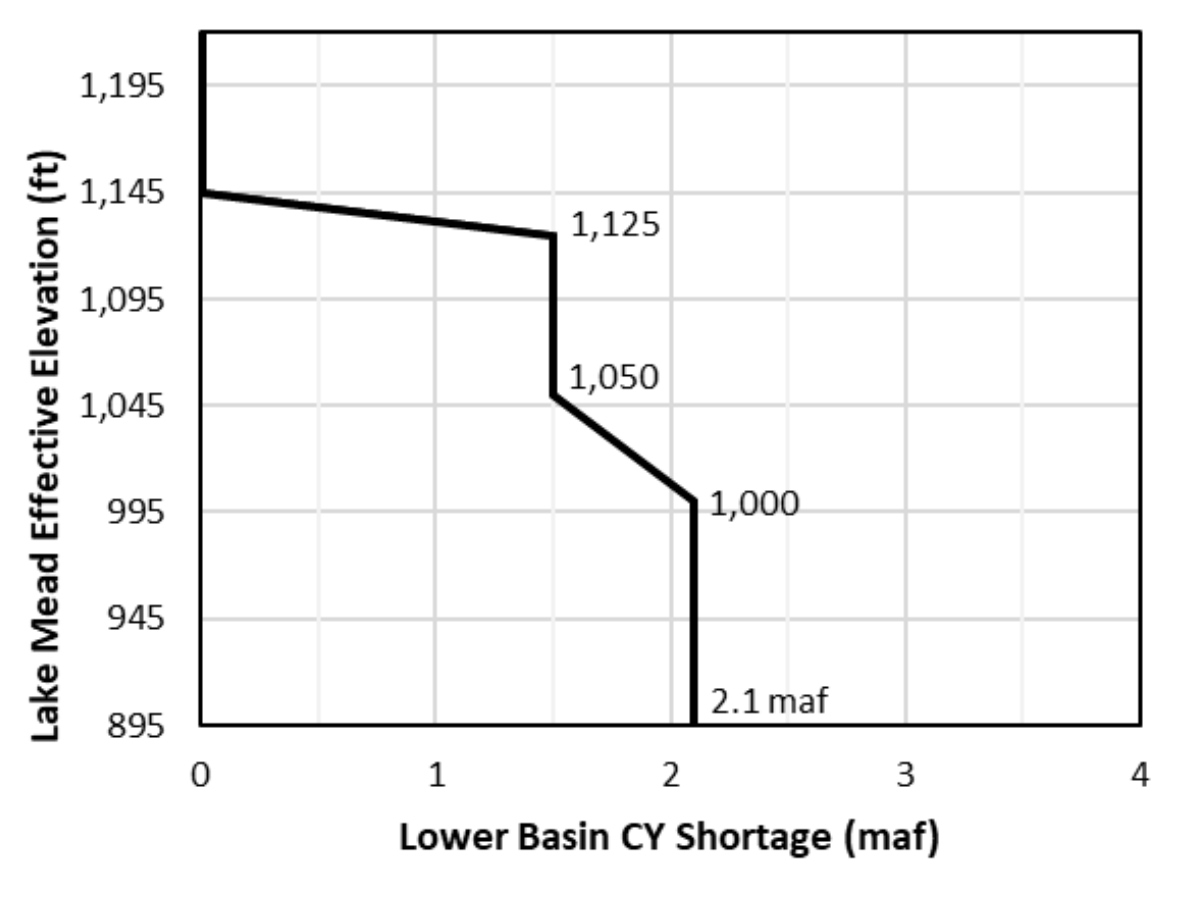
- Shortages determined based on Lake Mead elevation
- Shortages start at 1,145 feet and reach a maximum of 2.1 maf at 1,000 feet and below
Coordinated Reservoir Operations (Lake Powell and Lake Mead)
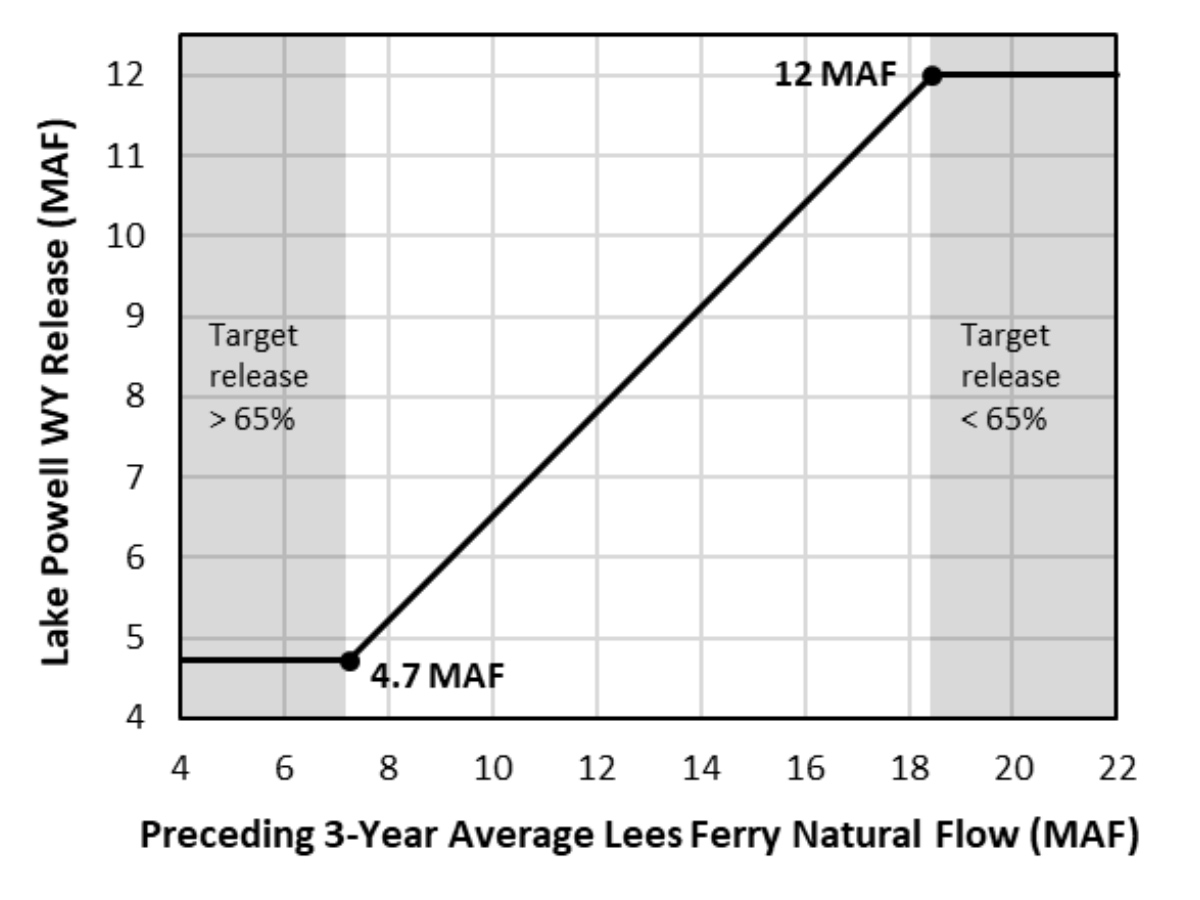
- Lake Powell releases determined primarily based on 65% of 3-year natural flows at Lees Ferry
- Releases range from 12.0 to 4.7 maf
Storage and Delivery of Conserved System and Non-system Water (Lake Mead and/or Lake Powell)³
- Storage up to 8.0 maf in Lake Mead; excluded for purposes of determining shortages
- Storage up to 3.0 maf at Lake Powell; included for purposes of determining Lake Powell releases
- Existing ICS converted to new mechanism over 10 years
- Expanded flexibilities: interstate exchanges within each basin
Surplus Guidelines to Increase Deliveries/Releases from Lake Mead³
- Surplus determinations based on Lake Mead elevation at or above 1,165 feet, 70R (spill avoidance strategy) or Flood Control conditions
Additional Activities Above Lake Powell
- Increased releases from CRSP Upper Initial Units by up to 500 kaf per year within their respective RODs and contingent on hydrologic conditions to protect infrastructure at Glen Canyon Dam
- Up to 200 kaf of Upper Basin annual conservation based on hydrologic conditions contributed to the Lake Powell conservation pool
- In years when Lake Powell cannot meet its required water year release because of low elevation, additional “gap water” is introduced into the system and tracked to be released in subsequent years
³ These operational elements contain modeling assumptions for water deliveries to Mexico. Shortage volumes include assumptions related to reductions in water deliveries to Mexico. Lake Mead storage volumes for the Storage and Delivery of Conserved System and Non-system Water include assumptions related to storage available to Mexico. Surplus Guidelines include assumptions related to increased deliveries to Mexico. Appendix A provides additional detail. Reclamation's modeling assumptions are not intended to constitute an interpretation or application of the 1944 Water Treaty or to represent current United States policy or a determination of future United States policy regarding deliveries to Mexico. The United States will conduct all necessary and appropriate discussions regarding the proposed federal action and implementation of the 1944 Water Treaty with Mexico through the IBWC in consultation with the Department of State.